Have you ever noticed this? Your search for a laptop in Google and every other website you visit after that has laptop advertisements. Instagram and Facebook feeds are also filled with the same.
Have you ever wondered how this happens? This is through a straightforward practice called cross-website tracking.
Cross-website tracking is when web developers track you down as you move from one website to another. Knowing your preferences and searches, the feed of your websites is customized accordingly.
This may sound strange until we get to the bottom of this. So this article will explain everything about cross-website tracking and how it works. Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- Cross-website tracking: Definition
- What is the need for Cross-website tracking?
- How does Cross-website tracking works?
- Privacy and security impacts of Cross-Website Tracking
- Cons of cross-website tracking
- Ways to stop cross-website tracking
- Mitigating the Effects of Cross-Website Tracking
Cross-website Tracking: Definition
As the term suggests, cross-website tracking is when website developers track an individual’s behavior while using any website. Through this, one can even track the activities of a person moving from one website to another.
Trackers who observe your activity usually collect data from your web searches and history. The collected data could be your search history, the sites you visit, your clicks on the website, and so on.
When the websites you visit have been enabled, third-party trackers can share the data collected from users with third parties. The data collected is usually used to improve the user experience and to offer customization to all users.
Cross-website tracking may not be acceptable to all common people. But when questioned, web developers and companies sought to provide reasons such as improving the website, giving a better user experience, customization of products, etc.
There could be many more reasons, but is cross-website really required at present?
What is the need for Cross-website tracking?
There isn’t any high-end reason to support the purpose the reason of cross-website tracking by the website developers. It is obvious that this is used to monitor the behavior patterns of every user while using any website.
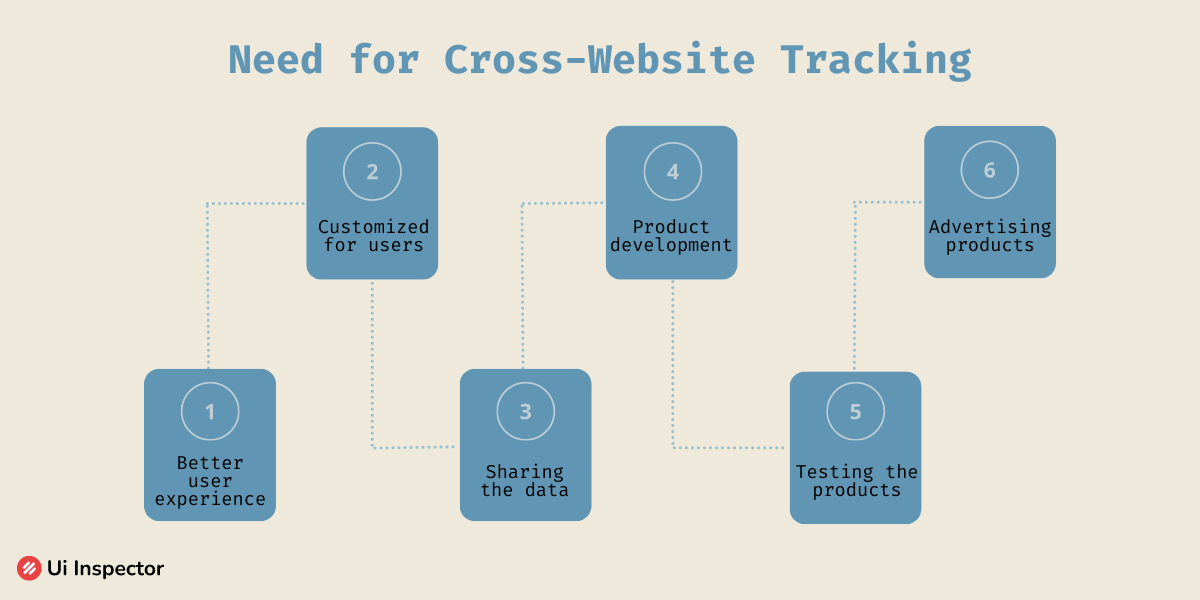
- Advertising: Cross-website tracking allows advertisers to gather data about user's browsing habits and interests, which can be used to serve targeted ads. This enables advertisers to reach a more relevant audience, increasing the effectiveness of their advertising campaigns.
- Personalization: By tracking user behavior across different websites, companies can create more personalized user experiences. For example, they can recommend products or services based on users' past purchases or browsing history.
- Analytics: Cross-website tracking can provide valuable data for website owners and businesses, such as how users interact with their website, what pages are most popular, and how long users stay on their site.
- Fraud prevention: Cross-website tracking can be used to detect fraudulent activity, such as bot traffic or click fraud. By monitoring user behavior across multiple sites, companies can identify patterns of suspicious activity and take action to prevent it.
- User identification: Cross-website tracking can identify users across different devices and platforms, allowing companies to create a more unified view of their customers.
- Affiliate marketing: Cross-website tracking is used in affiliate marketing to track referrals and commissions. By tracking users' activity across multiple sites, companies can accurately attribute referrals and ensure that affiliates are paid for their efforts.
How does Cross-website tracking work?
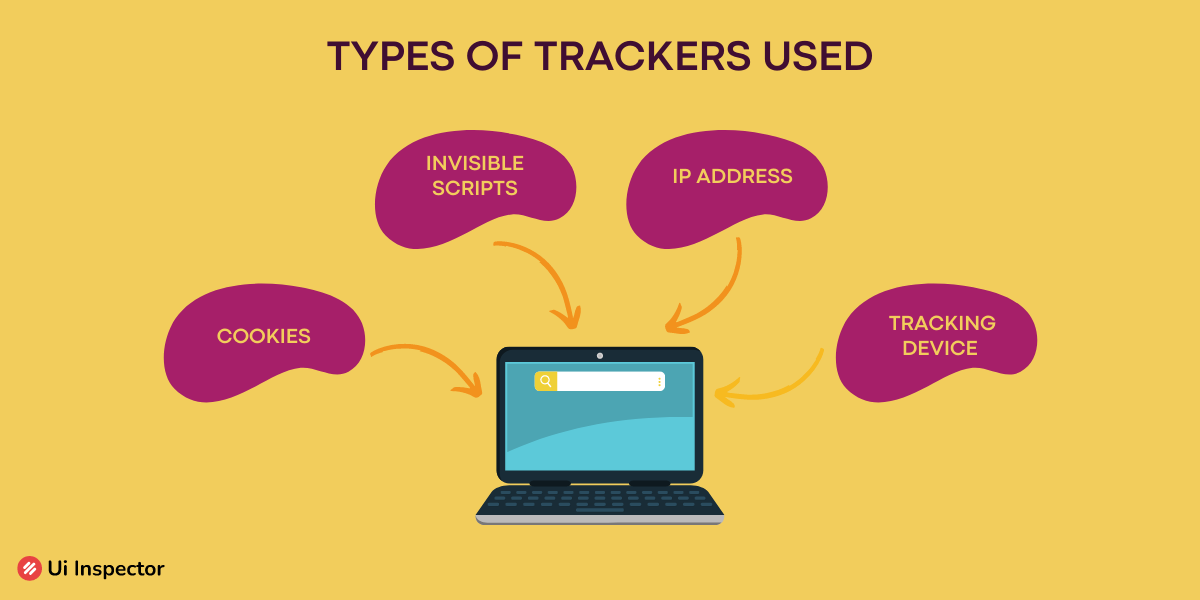
Now that we know what is being done under cross-website tracking let us look into how it works in reality. There are different types of such trackers being used:
- Cookies
- Invisible scrips
- IP address
- Website tracking devices
- Website logs
- Browsing history
The information collected from these trackers is the basis of tracking. The data is stored and used for providing the same set of preferences in your further searches and feed.
When a company wishes to track your searches, then they implant the cookie files or invisible scripts onto their websites. As soon as you enter their website and accept all the cookie files, the tracking begins, and it continues to your further searches.
On observing your other search patterns and history, the company gets an idea of your preferences. Based on all the collected information, digital agencies start sending advertisements to personalize your further browsing experiences.
We would have also noticed share buttons on the pages we visit. The share buttons are embedded to obtain the page analytics, but apart from that, for every click, a piece of information is shared with the owners of the page.
Likewise, the share, comment, and like buttons in social media buttons are also embedded with trackers to customize your feed accordingly.
Types of trackers
There are certain types of trackers that have been implanted in websites that are used to collect information effectively. The types of trackers are as follows:
1. Cookies
Every time you enter a new website, you have a popup message that shows, “This website uses cookies to optimize our website and our services; accept all cookies or decline.” That’s a kind of tracker that you allow and lets the digital agencies track your search history.
Cookies are like hints that you leave every time you visit a website. The web servers collect these hits, gather and make them in the form of a log which is being exploited for web optimization and customization.
What exactly happens when you start accepting cookies is that a piece of your browsing data, such as search patterns, is transferred from your data to the web server and is stored. This cookie data stores and remembers the data, which is used in the later part of your web searches, ad advertisements, or popups.
There are different types of cookies that are used for various functions in a web server.

- First-party cookies: This type of cookie is being implanted on the website by the domain and the owner.
- Third-party cookies: This is being embedded in the domain of the website as well as from remote domains. They can also collect data from your browsing patterns and store it.
- Persistent cookies: This type of cookie is a matter of concern because they remain in your server even after exiting the website. Persistent cookie track you down to other websites and collect data to send them to the web servers.
2. Web beacon
The next type of tracker is called the web beacon, which is a graphic image that is embedded in the website to track its users. It's a single-pixel (1x1 pixel) clear file that does function similarly to a website cookie.
The ad recommendations that are present are because of the web beacons. The role of web beacons is to travel and track our activities from one website to another. By doing so, from the collected data, new advertisements are displayed based on our browsing preferences.
This type of tracker is used to help advertising agencies. Using web beacons, companies can also track the success of their advertising campaign and obtain analytics.
Apart from this, when a web beacon is embedded in a spam email, then when you open that email, the beacon can track your IP address. From this, similar kinds of emails are sent to us from the collected data.
3. Canvas fingerprinting
The before mentioned trackers were used to collect statistical information related to the browsing history of a user. When the same browsing pattern is converted to a graphical representation, then it is called Canvas fingerprinting.
When canvas fingerprinting is enabled in your browser, then an image is drawn, which acts as a graphics card. This graphics card is unique for every user and periodically monitors the browsing behavior of the users. Since this differs for every individual, it is referred to as a fingerprint.
Privacy and security impacts of Cross-Website Tracking
Cross-website tracking can have significant impacts on both privacy and security online. Here are some key points to consider:
Privacy Impacts:
- Cross-website tracking can reveal a user's browsing habits, personal preferences, and other sensitive information, which can be used to create detailed profiles and targeted advertisements.
- The use of third-party cookies and other tracking technologies can allow companies and advertisers to track users across multiple websites without their explicit consent or knowledge.
- Data collected through cross-website tracking can be vulnerable to data breaches, hacking, and other forms of cyber attacks, putting users' personal information at risk.
- Cross-website tracking can also raise ethical concerns around the collection and use of personal data and may be perceived as a violation of users' privacy rights.
Security Impacts:
- Cross-website tracking can be exploited by malicious actors for phishing attacks, malware distribution, or other scams, as they can use the collected data to target specific individuals with highly personalized attacks.
- Tracking data can also be used to build detailed profiles of users, which can be sold on the dark web and used for identity theft or other fraudulent activities.
- The use of third-party cookies and other tracking technologies can create vulnerabilities that can be exploited by hackers to gain unauthorized access to a user's device or account.
Cons of cross-website tracking
There could be various reasons to justify the implementation of cross-website tracking. But still, it is related to the privacy of every user, so closer observation and importance should be given to its limits.
Every individual visits various websites every day, and letting the web owners track is like allowing multiple agencies to track your browsing pattern in a day. Not knowing how much data is being collected is a matter of concern.
The users aren’t very transparent about how their data is being used. Every piece of information collected requires consent, and these trackers are embedded automatically, which tests privacy-related issues.
The next biggest problem is third-party cookies. The session and persistent cookies present in the browser expire after the expiration date. But the third-party cookies stay in the browser, and the information is shared with other parties except for the domain.
To the rules and regulations of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), it is mandatory for digital agencies to obtain consent from users before tracking their browsing analytics.
Ways to stop cross-website tracking
There is a method to prevent the web servers to track your browsing pattern from google chrome. The steps are as follows:
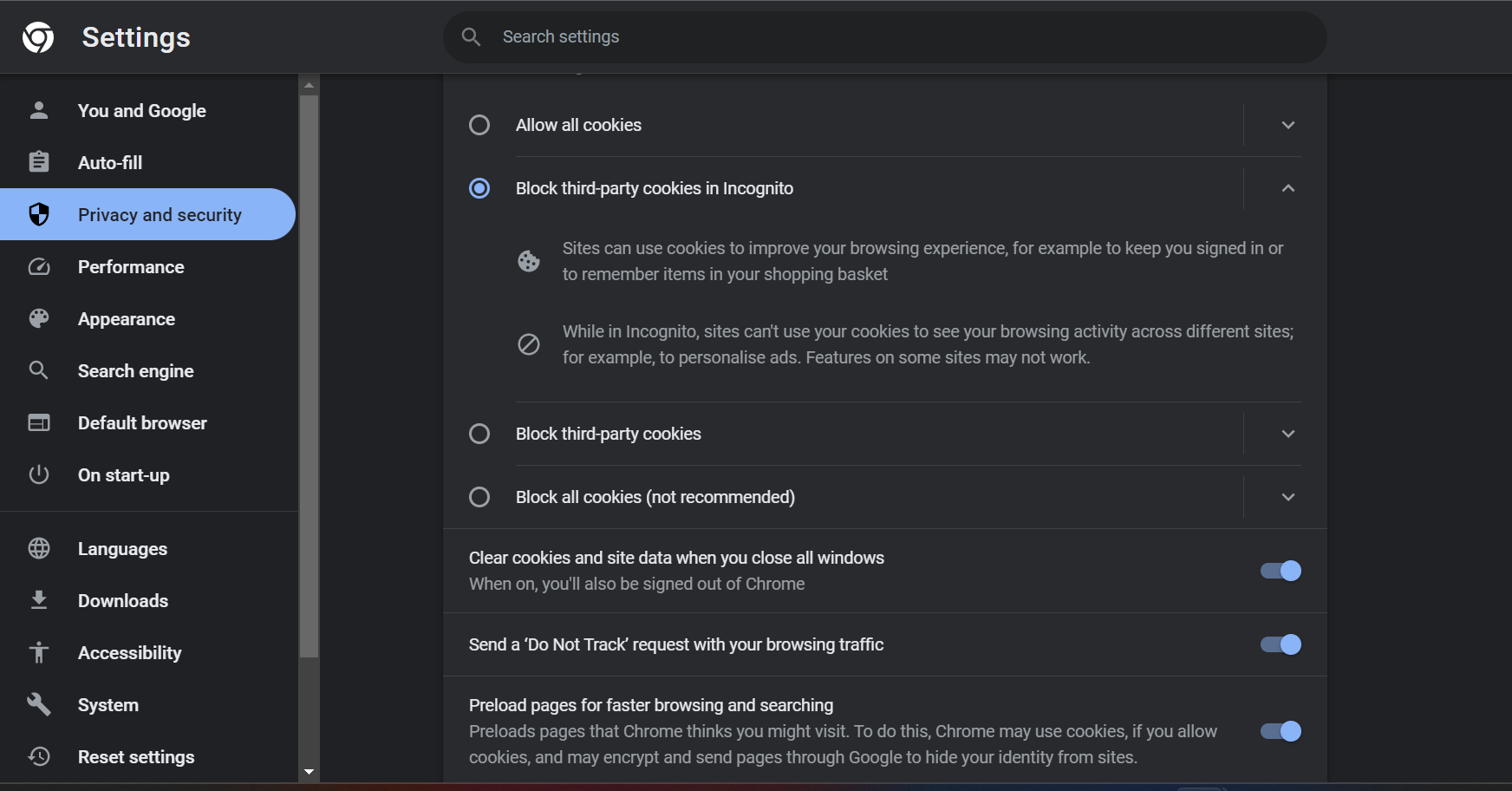
- Open the Chrome app on your desktop
- On the right corner of the screen, you will find three dots.
- Click the settings option.
- Go to the privacy and security option and choose cookies and other site data.
- Click "clear cookies and site data when you close all windows".
- By doing so, you can prevent cookies to track your device.
Mitigating the Effects of Cross-Website Tracking
To mitigate the effects of cross-website tracking, here are some steps that individuals can take to protect their privacy and security online:
- Use Privacy-Focused Browsers and Extensions: Some web browsers, such as Firefox and Brave, have built-in privacy features that block third-party cookies and prevent cross-website tracking. Additionally, there are browser extensions, like Privacy Badger and uBlock Origin, that can also help block tracking technologies.
- Disable Third-Party Cookies: Users can disable third-party cookies in their web browser settings to prevent websites from tracking their activity across the web. However, some websites may not function properly without cookies, so users may need to enable them on a case-by-case basis.
- Use Private Browsing Mode: Most web browsers have a private browsing mode that does not save browsing history, cookies, or other data. This can be a good option for users who want to prevent websites from tracking their activity.
- Limit the Information You Share Online: Users can limit the amount of personal information they share online, including on social media and other websites. This can help reduce the amount of data that is collected and used for cross-website tracking.
- Be Cautious of Clicking on Links or Downloading Attachments: Cross-website tracking data can be used to create highly personalized phishing attacks or other scams, so users should be cautious when clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
- Support Industry Efforts to Improve Privacy: Users can support industry efforts to improve privacy by using services and products that prioritize user privacy and advocating for stronger regulations and standards around cross-website tracking.
Sum up
In recent times everybody expects customization and personalization of products. We also demand easier and simpler living with the ease of the internet and website innovations.
This interest of ours has let web owners and digital agencies deliver what is desired by every individual. On this note, cross-website tracking is justifiable from their perspective. But for certain users, it can be invading their personal space.
Unless it is in a limited amount, the tracking can be used for building our feed. But when it starts to violate privacy, then it is a serious issue, and action is being taken. So know what cookies you are accepting and change them to avoid further problems.
Boost your Testing Efficiency with UI Inspector
UI Inspector is a cloud-based cross-browser testing platform that allows developers and testers to test their web applications on a wide range of real devices and browsers. With Ui Inspector, teams can ensure their applications work seamlessly across multiple platforms, browsers, and devices and provide a better user experience for their customers.
It has an intuitive interface, which requires no coding skills to operate. This allows testers and developers of all skill levels to create and execute automated tests quickly and easily.
UI Inspector provides an efficient and reliable solution for cross-browser testing, helping teams deliver high-quality applications that work seamlessly across all devices and platforms. Its extensive device and browser coverage, seamless integrations, and range of features make it a valuable tool for any development or testing team looking to improve its testing process and deliver better user experiences.
Our solutions include Test Automation, API testing, Data-driven testing, Cross browser testing, etc., to make the testing procedures easier. Find out the suitable testing tool for your software.
Sign up now for UI Inspector's 14-day free trial offer and experience the power of its features to discover limitless possibilities!

